Care Facility Managers' Guide to Handling Care Accidents: From Prevention to Response

In light of the recent increase in accidents in the caregiving sector, more facility managers are seeking to reconstruct their accident response manuals to better address these incidents. It is imperative to develop prevention measures and create response manuals that align with current trends for handling accidents in caregiving facilities. Owners and managers of caregiving facilities must accurately understand the procedures necessary for this purpose.
This article provides detailed explanations on key points for creating an accident response manual tailored for caregiving facility managers, strategies for preventing caregiving accidents, and how to handle incidents when they occur. Use this information as a reference to minimize the risk of caregiving accidents and to provide a safer caregiving environment.
Overview and Reality of Nursing Care Accidents in Japan

Nursing care accidents refer to all personal accidents that occur during the provision of welfare services, resulting in physical or mental harm. These incidents are typically treated as accidents regardless of whether there is any error or negligence on the part of the service provider.
Here, we will provide a detailed explanation of the basic overview and reality of nursing care accidents in Japan.
Definition of Nursing Care Accidents Under Japanese Law
According to materials from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (Note 1), the definition of “nursing care accidents” is quoted from the “Collection of Welfare Service Accident Cases” by the National Council of Social Welfare, stating that it encompasses “all personal accidents that occur throughout the entire process of welfare services in social welfare facilities, resulting in physical and mental harm, regardless of the presence of error or negligence on the part of the service provider.”
When a nursing care accident occurs, it is important to note that responsibility extends to both the “facility” and the “employees.” Facilities may be liable for damages due to breach of the duty of care or breach of the duty of attention (Civil Code Article 415, Paragraph 1, and Article 709) as well as employer liability (Civil Code Article 715, Paragraph 1) and liability for defects in property (Civil Code Article 717, Paragraph 1).
In addition, administrative responsibilities must be considered, such as the revocation of designation under the Long-Term Care Insurance Law (Long-Term Care Insurance Law Article 77, Paragraph 1, etc.), which may be imposed as a measure.
On the other hand, employees may be held criminally responsible for damages based on tort (Civil Code Article 709) or for the crime of negligence resulting in injury during the course of work (Penal Code Article 211).
Note 1: Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan | About the Guidelines for Crisis Management (Risk Management) in Welfare Services – Seeking the Smiles and Satisfaction of Users
Main Types of Accidents in Caregiving
In the caregiving field, understanding the various risks of accidents and taking preventive measures to ensure the safety of users is crucial. Here, we will explain the main types of accidents that occur in caregiving.
[Falls and Tumbles]Falls and tumbles are the most common accidents in caregiving settings. They occur when someone stumbles and loses their balance or falls from a bed or chair. These accidents are particularly common among the elderly and those with weak legs or instability.
[Choking Accidents]Choking accidents happen when food or drink is accidentally inhaled into the trachea. This is often seen in elderly individuals with diminished swallowing functions, increasing the risk of suffocation or pneumonia, thus requiring proper meal assistance.
[Medication Errors]Medication errors occur when the wrong medication or dosage is administered. These can happen due to poor medication management or insufficient information sharing and can directly affect the health of the user, necessitating caution.
[Fires and Burns]Fires and burns refer to accidents involving fires in facilities or users sustaining burns. Causes can include forgetting to turn off the stove while cooking or malfunctioning water heaters. To minimize damage, thorough preventive measures are essential.
Incidence and Statistics of Accidents in Japanese Caregiving
To understand the reality of accidents in caregiving, it is essential to analyze statistical data. Here, we will provide an overview of the occurrence of caregiving accidents based on the survey results conducted by the Public Interest Incorporated Foundation Care Work Foundation.
The survey targeted 276 cases of caregiving accidents that occurred from August 15, 2014 (Heisei 26), to February 27, 2017 (Heisei 29). The cases in question are serious incidents reported to the Consumer Affairs Agency in Japan, generally involving hospitalization for 30 days or more.
[Classification of Accident Situations]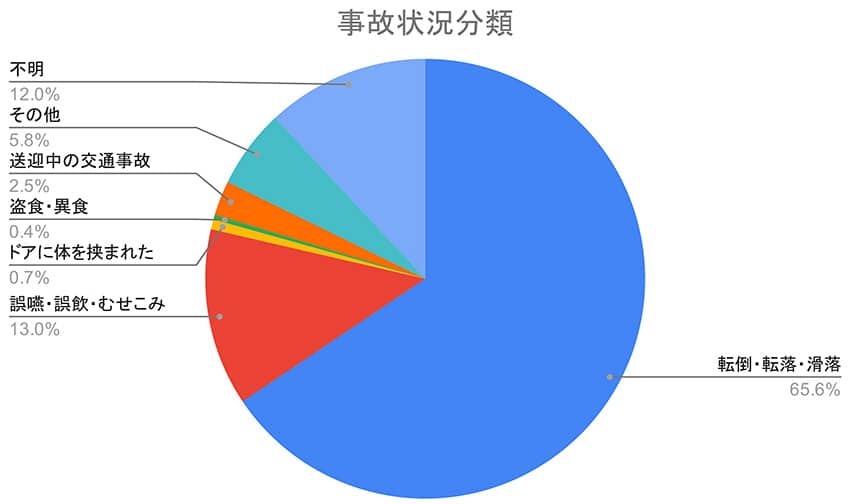
| Falls, Drops, and Slips | 65.6% |
| Choking, Mis-swallowing, and Suffocation | 13.0% |
| Body Caught in Door | 0.7% |
| Stealing or Eating Inedible Objects | 0.4% |
| Accidents During Transportation | 2.5% |
| Other | 5.8% |
| Unknown | 12.0% |
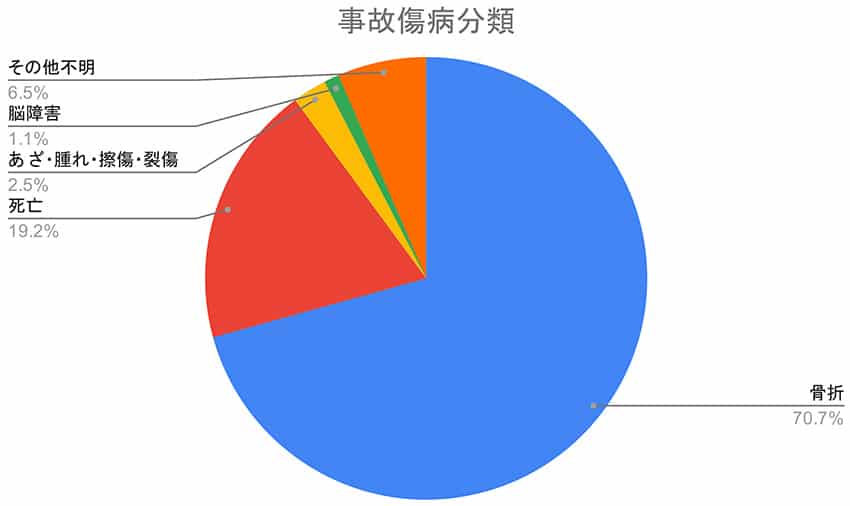
| Fractures | 70.7% |
| Deaths | 19.2% |
| Bruises, Swellings, Abrasions, Lacerations | 2.5% |
| Brain Injuries | 1.1% |
| Other Unknown | 6.5% |
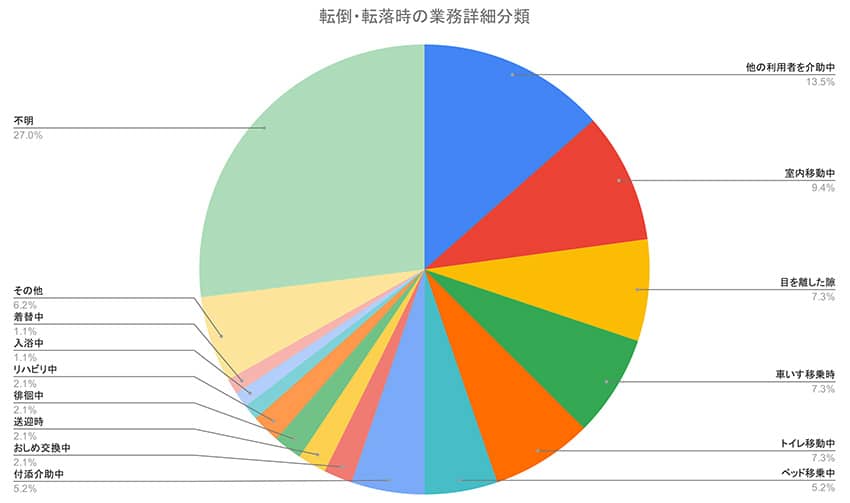
| During Supervision | 46.7% |
| While Assisting Other Clients | 7.2% |
| During Indoor Movement | 5.0% |
| While Not Being Watched | 3.9% |
| During Wheelchair Transfers | 3.9% |
| During Toilet Transfers | 3.9% |
| During Bed Transfers | 2.8% |
| While Accompanying Assistance | 2.8% |
| During Diaper Changes | 1.1% |
| During Transportation | 1.1% |
| During Wandering | 1.1% |
| During Rehabilitation | 1.1% |
| During Excretion | 0.6% |
| During Bathing | 0.6% |
| During Dressing | 0.6% |
| Other | 3.3% |
| Unknown | 14.4% |
Reference: Public Interest Incorporated Foundation Care Work Foundation | “Research Project on the Prevention of Accidents Related to the Use of Care Services” Report
Key Points in Creating a Response Manual for Incidents in Japan

In the field of caregiving, it is unpredictable when, where, and what kind of accidents may occur. Falls, choking, and medication errors are just a few examples of the various types of caregiving accidents that can happen, and in the event of such incidents, there is a risk of serious impact on the life and health of the service users.
Therefore, it is essential for caregiving service providers to have a manual in place that defines the appropriate procedures for responding to accidents. Here, we will explain the key points in creating such a manual.
The Importance of Initial Response
Providing a prompt and appropriate initial response when an incident occurs is crucial to prevent the situation from escalating and to minimize damage. The first priority must always be to ensure the safety of those involved. Specifically, this involves quickly understanding the situation and taking the right measures. For example, assessing the extent of any injuries to individuals and, if necessary, performing first aid such as applying pressure to stop bleeding, administering artificial respiration, or performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
Depending on the condition of the individuals involved, it may also be necessary to call emergency services at 119 promptly and arrange for an ambulance. By thoroughly implementing these initial responses, the impact of the accident can be minimized, leading to a swift post-incident handling.
Furthermore, it is essential not to forget to report to superiors and confirm instructions, ensuring an organized response as a company. Appropriate initial response is the first step in protecting the safety of those involved.
Establishing a Reporting and Communication System
For a swift response to incidents in caregiving, it is essential to establish a clear reporting and communication system, enabling effective initial responses through a comprehensive understanding of the procedures by all staff members.
First and foremost, the development of an emergency contact network is crucial. The communication system, including managers, must be available 24 hours a day, and the chain of command during the manager’s absence must also be clearly defined.
Next are the procedures for contacting relevant organizations. In the event of a fatality, you must report to the police station; for infectious diseases and food poisoning, the public health center; and for all accidents, the insurer in the location of the facility and the insurer of the user must be notified. Prepare a list of these contacts, reporting criteria, and forms in advance.
Furthermore, it is imperative to promptly contact the families of the users. It is important to explain the details of the accident and the condition of the user in an understandable manner, striving to gain their understanding and consent.
Reference: Fukuoka Prefecture Long-Term Care Insurance Wide Area Union | Guidelines for Creating a Manual on Preventing Caregiving Accidents
Responding to and Explaining to Families
After an incident occurs, it is crucial to explain the details of the accident and the measures taken to the client’s family promptly and courteously.
Firstly, immediately after the accident, it is essential to report that appropriate initial responses have been taken and to accurately convey the subsequent situation and measures implemented. During this time, to alleviate the family’s anxiety and gain their understanding, explanations should be delivered in a calm tone.
Next, when explaining to the family, it is important to maintain an attitude of honesty and accuracy without downplaying the facts. Regardless of the presence or absence of liability for the accident, building a trusting relationship is possible by empathizing with the family’s emotions, offering a moral apology, and presenting concrete measures.
In this process, care must be taken to ensure the accuracy of information, as conveying facts ambiguously, even unintentionally, may lead to future troubles.
Finally, to maintain close communication with the family, it is vital to designate a clear point of contact and ensure consistent responses as an organization. By centralizing the point of contact, explanations and responses to the family’s questions can be managed smoothly, thereby enhancing the credibility of the service provider.
How to Create an Accident Report in Japan
If an accident occurs during the provision of services, it is mandatory to promptly submit an “Accident Report” to the local municipality. The specific reporting destination varies by local government.
Here, we will take Kita Ward in Tokyo as an example. In Kita Ward, the reporting destination is the “Kita Ward Office Welfare Department Long-Term Care Insurance Section Benefit Adjustment Division Accident Report Contact“. The format for the accident report can be downloaded as an Excel file from Kita Ward’s official website, and it is to be submitted via email.
The contents to be included in the accident report are as follows:
- Details of the accident situation
- Overview of the office
- Individual(s) involved
- Summary of the accident
- Response at the time of the accident
- Post-accident situation
- Analysis of the cause of the accident (analysis of factors related to the individual, staff, and environment)
- Measures to prevent recurrence (changes in procedures, environmental changes, other responses, and the timing and results of the evaluation of the preventive measures)
- Status of compensation for damages (if applicable, include details)
- Other matters worth noting
In addition, for serious accidents or those requiring urgent attention, it is necessary to report by phone to the Long-Term Care Insurance Section Benefit Adjustment Division as soon as possible. If the report is delayed, a Delay Reason Statement (in any format) must be attached. Furthermore, the initial report should include at least items 1 through 6, and it should be submitted as soon as possible after the accident, ideally within 5 days.
Accident Prevention Strategies for Staff Training

Staff training for accident prevention in caregiving facilities is essential to reduce actual incidents in the field. Daily operations require initiatives to enhance staff awareness and responsiveness through the use of near-miss cases, risk assessments, and improvements in communication.
Here, we will introduce in detail the methods for sharing specific examples and conducting exercises that can be utilized in staff training as accident prevention strategies.
Utilizing Near-Miss Incidents in Caregiving
Sharing near-miss incidents is an extremely effective method for preventing accidents in caregiving settings. These are events that did not result in an accident but could have led to a serious situation if one more mistake had been made. By sharing and analyzing such incidents among staff, it is possible to prevent accidents before they occur.
For example, to prevent medication errors, implementing a double-check by two staff members and ensuring proper identification of the individual can serve as preventive measures. To reduce the risk of wheelchair users falling, checking for uneven surfaces and adjusting speed are important. For preventing falls during bathing, thorough assistance, the use of non-slip mats, and keeping the floors clean are effective strategies.
Through these examples, staff can learn specific points of caution and enhance their awareness of accident prevention.
Methods of Conducting Risk Assessments
Risk assessment is a method of identifying and evaluating accident risks in the workplace in advance and implementing preventive measures according to their significance. The general process for conducting a risk assessment is as follows.
[Implementation of Risk Assessment]| Step | Details |
| 1. Identification of Hazards or Harmfulness | Identify hazards or harmfulness for each task. |
| 2. Risk Estimation | Use risk estimation methods to assess the risk of disasters that are expected to occur due to the identified hazards or harmfulness. |
| 3. Consideration of Risk Reduction Measures | Set priorities and consider measures in the following order: |
| 1. Inherent Measures (elimination of hazardous work, design changes, etc.) | |
| 2. Engineering Measures (use of welfare equipment) | |
| 3. Administrative Measures (creation of work procedures, education, etc.) | |
| 4. Use of Personal Protective Equipment | |
| 4. Implementation of Risk Reduction Measures | After implementing risk reduction measures, re-estimate the risk and pay attention to any residual risks. |
| 5. Recording of Results | Accumulate and pass on know-how for future risk management. |
Exercises for Improving Communication
Exercises aimed at improving communication among staff members can have a significant impact on accident prevention. It is crucial to ensure thorough information sharing among staff through regular exercises. For instance, organize review meetings for near-miss incidents and accident cases, where everyone can exchange opinions on the causes and countermeasures.
By enhancing communication among staff, the perception that accidents are not solely the responsibility of individual employees but rather an issue for the entire organization can be fostered. Additionally, listening to perspectives from other staff members can help identify areas for improvement in one’s own duties.
Furthermore, it is vital that exercises help build trust among staff members. By establishing regular opportunities for communication, everyday information sharing becomes more efficient, enabling early detection and response to hazardous situations.
If collaboration in daily operations is strengthened, cooperation among staff members during actual accidents can become more rapid and effective.
As outlined above, exercises for improving communication are essential for ensuring thorough information sharing and smooth responses in the event of accidents. By raising each staff member’s awareness towards accident prevention, an overall enhancement in the safety of the facility can be expected.
Case Studies Using Accident Examples
In staff training, case studies that utilize past accident examples are extremely effective in enhancing the response capabilities of employees.
First, it is crucial to thoroughly understand the details of the accident and to meticulously investigate the causes. For instance, in the case of a slip and fall accident, it is not enough to simply have ‘staff accompany’ the individual; there is a need to consider more effective measures such as checking the condition of the floor and removing any obstacles.
Next, we develop measures to prevent recurrence and verify their effectiveness. For example, by reviewing the arrangement of electrical cords, efficient and prompt responses can be made possible.
Understanding concrete response measures through learning from actual accidents and acquiring practical accident prevention skills is important.
Creating a Checklist to Prevent Accidents in Caregiving
According to the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare’s discussion on the development of a “Draft Checklist for Preventing Accidents in Caregiving” (link to the document), a draft checklist has been proposed. Please consider utilizing this checklist when creating or reviewing one for your own facility.
| Main Category | Subcategory |
| 1. Initiatives to Prevent Accidents | 1-1. There are measures in place to prevent accidents |
| 1-2. Conduct risk assessments for each resident and implement interventions | |
| 2. Staff Education & Training | 2-1. There is a systematic education program for new staff |
| 2-2. Staff training and study sessions are conducted in a planned manner | |
| 2-3. External training on safety and infection control is utilized | |
| 3. Environmental Arrangements | 3-1. The environment is arranged with accident prevention in mind |
| 3-2. The environment is arranged with consideration for infection and hygiene | |
| 4. Response to Accidents | 4-1. Appropriate responses are in place for when accidents occur |
| 4-2. The causes of accidents are analyzed, and efforts are made to prevent recurrence | |
| 4-3. There is a system to evaluate recurrence prevention measures after a certain period | |
| 5. Falls and Tumbles | 5-1. Conduct risk assessments for each resident and implement interventions |
| 5-2. Implement protocols and procedures based on best practice guidelines | |
| 5-3. Conduct education on preventing falls and tumbles | |
| 5-4. Evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk assessment indicators and protocols | |
| 6. Accidents During Bathing | 6-1. Efforts are made to prevent accidents during bathing |
| 6-2. Efforts are made to prevent scalding during bathing | |
| 7. Emergency Response | 7-1. A system is in place to respond appropriately in case of emergencies |
| 7-2. Appropriate responses are in place for disasters |
Reference: Longevity Science Policy Research Project, Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare | Discussion on the development of a “Draft Checklist for Preventing Accidents in Caregiving” (link to the document)
Checkpoints for Reviewing Safety Measures in Facilities

Revising safety measures in caregiving facilities is essential to protect the safety and health of the users. A thorough review of the facility’s environment, assistance techniques, medication management, and infection control measures is required. Here, we will explain in detail the specific points and methods of implementing these measures.
Key Points in Environmental Preparation
Environmental preparation in caregiving facilities is crucial for reducing the risk of falls and accidents. Below are specific points to consider.
Clarification of Objectives
The purpose of environmental preparation is to provide a safe space for users. By doing so, it aims to prevent accidents before they occur.
Specific Preparation Points
| Item | Details |
| Adoption of Universal Design | Create an environment that is easy to use for all users. Consider equity and safety by eliminating steps and installing handrails. |
| Improvement of Flooring and Lighting | Use non-slip flooring materials and install appropriate lighting. These measures enhance visibility and reduce the risk of falls. |
| Ensuring Passage Ways | Ensure wide passageways that are easy to navigate with wheelchairs, enabling smooth movement. |
| Inspection of Hazardous Areas | Regularly inspect the facility to identify and improve hazardous areas. Review and address equipment malfunctions and procedural issues. |
| Meticulous Organization | Maintain the facility in a consistently clean and organized state. Promptly deal with fallen papers or wet floors and install anti-slip mats. |
Verification and Improvement of Effects
After preparation, regularly verify the effectiveness and make improvements as necessary. These improvements help maintain the latest safety standards at all times.
Revisiting Caregiving Techniques
In order to prevent accidents in caregiving facilities, it is essential to regularly review the caregiving techniques of staff members and ensure they acquire the appropriate skills. Strive to provide high-quality services by mastering these skills and securing the safety of the users.
The Importance of Reviewing Techniques
Revisiting caregiving techniques helps prevent overlooking risks and clarifies problem areas, leading to improvements in service delivery.
Specific Initiatives
| Item | Details |
| Establishing Basic Service Delivery Methods | Set clear, documented methods to maintain a consistent level of service quality. |
| Sharing User Information | Accurately record the physical and mental condition of users and share the information among relevant parties. Review caregiving methods as necessary. |
| Ensuring Awareness of the Accident Prevention Manual | Make sure all staff are aware of the manual and deepen their understanding through training. Develop the ability to respond flexibly to various situations. |
| Conducting Regular Training | Provide training not only at the time of new hires but also on a regular basis. Conduct training as needed in the event of an accident to improve staff awareness. |
| Emergency Response Training | Train to calmly respond in emergencies, such as performing artificial respiration or using an AED. |
Through these initiatives, let’s maintain the caregiving techniques of staff members at their most current and appropriate state and strive to prevent accidents.
Rigorous Medication Management
Rigorous medication management is crucial to prevent medication errors. It is essential to clarify the methods of managing medications and the procedures for verification to ensure appropriate measures are taken.
Firstly, it is important to habitualize multiple checks when handling medications. Verify that the medication is correct at three key moments: when taking it out of the dispensing box or medication pouch, when handing it over to the patient, and before the patient takes it. Such verification can prevent medication errors due to human error. Checks by multiple staff members are also effective.
Next, it is vital to unify the rules regarding medication handling within the team. To prevent confusion during care that coincides with meal times or in situations where medication verification tends to be insufficient, rules must be clarified and understood by everyone.
Furthermore, ensure to confirm that the patient has swallowed the medication after putting it in their mouth. As there are cases where patients spit out the medication before swallowing, it is important to verify until the very end.
Finally, use checklists to regularly review the practices at the facility. By reviewing, you can maintain the most up-to-date management methods and minimize the risk of medication errors.
Enhancing Infectious Disease Control Measures in Care Facilities
Strengthening infectious disease control measures in care facilities is extremely important for protecting the health of the users. By regularly disinfecting and ensuring thorough handwashing, we aim to minimize the risk of infection.
Handwashing is the most basic and effective measure. Caregivers frequently engage in tasks with a high risk of infection, making hand hygiene management essential. Regular disinfection of facilities and medical equipment is also crucial. In particular, ensure thorough disinfection of areas that users frequently touch.
As a measure against droplet infection, it is also important for staff to wear masks and perform gargling. These practices help prevent the spread of infectious diseases. Furthermore, ensuring that everyone is fully aware of the infection control measures is vital. Through staff education and training, we can establish a system that always implements the latest measures.
In the event of an infectious disease outbreak, it is necessary to promptly contact the public health center and take appropriate measures. Additionally, it is advisable to have a ‘business continuity plan’ in place in advance, anticipating the possibility of staff infections.
Building a Risk Management System

Establishing a risk management system in caregiving facilities is essential to ensure the safety of users and provide high-quality services. Effective risk management requires organization-wide commitment and continuous improvement.
Here, we will explain specific strategies for building a risk management system.
Establishing a Risk Management Committee
To effectively promote risk management in nursing care facilities, it is crucial to build a system that involves the entire facility, and one effective means to achieve this is the establishment of a “Risk Management Committee.”
The Risk Management Committee is composed of various professionals including facility managers, caregivers, nurses, rehabilitation staff, and consultants. It examines risks from diverse perspectives to devise more effective measures.
The committee regularly holds meetings to engage in the following activities:
- Collecting instances of near-misses and accidents that occur within the facility, and analyzing their causes and backgrounds.
- Based on the analysis, considering measures to prevent accidents and creating specific action manuals.
- Disseminating the created manuals to staff and ensuring understanding and integration through training and other means.
- Conducting regular risk assessments to review existing measures and consider improvements.
By positioning the Risk Management Committee at the core of the organization, we carry out continuous and systematic risk management activities.
Continuous Improvement Using the PDCA Cycle
Risk management is not a one-time event. What is crucial is the continuous rotation of the PDCA cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Action) to enhance risk management and improve measures.
Specifically, it can be applied in the following ways when utilizing near-miss incidents:
- Cause analysis and measure planning (Plan)
- Implementation of measures (Do)
- Verification of effectiveness and evaluation (Check)
- Planning of improvement measures (Action)
By continuously operating this cycle, you can enhance your ability to respond to risks, suppress the occurrence of accidents, and, should an accident occur, enable a swift and appropriate response, leading to the prevention of recurrence.
To make the PDCA cycle function effectively, it is important to utilize organizations such as risk management committees and to regularly evaluate and improve the status of activities.
Utilizing External Experts
To build an effective risk management system, it is crucial to leverage the insights of external experts. Professionals such as attorneys analyze risks from a legal perspective and provide appropriate advice.
For example, by contracting an attorney well-versed in nursing care accidents as an advisory lawyer, you can benefit from their swift and appropriate response in the event of an accident.
Specifically, you can receive precise support in situations that require specialized knowledge and experience, such as initial responses to accidents, settlements with users or their families, and litigation.
Utilizing external experts not only strengthens the risk management system of the facility but also reduces the psychological burden on staff. With the support of experts, create an environment where facility staff can focus on their duties with peace of mind.
Enhancing Safety Management through the Adoption of ICT Devices
The introduction of ICT devices in the caregiving field significantly contributes to the strengthening of risk management systems. Specifically, this includes nurse call systems, monitoring camera systems, area detection systems, and business management support services.
These systems ensure the safety of users while simultaneously improving staff work efficiency. For example, monitoring camera systems can prevent accidents such as falls through AI-powered image analysis.
Furthermore, area detection systems instantly detect when users leave the building or enter hazardous areas and notify the staff.
In addition, business management support services can lead to a distribution of workloads and an improvement in the quality of care by digitizing staff movement data. The adoption of these ICT devices may also help alleviate staff shortages and increase staff retention rates.
Summary: Thoroughly Prevent and Prepare for Accidents in Care Facilities

To prevent accidents in care facilities and to respond swiftly and appropriately when they do occur, it is crucial to practice preventive measures daily and to enhance staff awareness. Understanding the nature of accidents and clarifying reporting systems and family response policies can strengthen your ability to respond.
Furthermore, a comprehensive approach is required, including establishing risk management systems, sharing accident prevention measures through training, and reviewing safety measures in facilities. By being thorough in these efforts, you can minimize the risk of accidents in care facilities and strive to provide a safer care environment.
Guidance on Measures by Our Firm
The caregiving industry in Japan is governed by a complex web of laws, including the Long-Term Care Insurance Act, the Elderly Welfare Act, and the Companies Act. Monolith Law Office serves as legal counsel for the National Association of Caregiving Service Providers and caregiving service providers across various prefectures, possessing extensive know-how related to laws concerning caregiving businesses.
Areas of practice at Monolith Law Office: Corporate Legal Services for IT & Startups
Category: General Corporate
Tag: General CorporateIPO





















