Key Points to Consider When Creating a GDPR-Compliant Privacy Policy

When handling the personal information of users within the EU domain, it is necessary to comply with the GDPR, and you must create a privacy policy that aligns with the GDPR. However, many may not fully understand the details of the GDPR, leaving them uncertain whether their own website needs to comply and, if so, how to go about it.
In this article, we will explain the basics of the GDPR and the key points in creating a GDPR-compliant privacy policy. We will also introduce the current state of compliance in Japan and provide examples from well-known companies, which you may find useful as a reference.
Understanding GDPR and Privacy Policies

What constitutes a GDPR-compliant privacy policy? In this section, we will explain the basics of the GDPR and the obligations of privacy policies under the GDPR.
GDPR and Privacy Policies
The GDPR is a regulation established by the EU that details the protection and handling of personal information. The GDPR applies within the European Economic Area (EEA), which includes EU member states, Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway, excluding Switzerland. Japanese companies may also be subject to GDPR in the following cases:
- Offering goods or services to data subjects within the EU
- Monitoring the behavior of data subjects within the EU
A data subject is an identified or identifiable natural person to whom the personal data relates.
Companies that fall under the above criteria must review and revise their privacy policies (privacy notices). In the event of a GDPR violation, they could face fines of up to 20 million euros or 4% of their global turnover, whichever is higher.
Reference: Japan External Trade Organization | “General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)”[ja]
To ensure safe transactions with EU countries, it is essential to verify your privacy policy.
‘Information Provision’ at the Time of Personal Data Acquisition as Stipulated by the GDPR
Under the GDPR, when acquiring personal data, the controller must provide certain information to the data subject, as stipulated in Article 12(1) of the GDPR, which describes the method of providing information.
The requirements are as follows:
- Concise, transparent, understandable, and easily accessible
- Using clear and plain language
- Taking appropriate measures when providing information to children
- Provided in writing, or by electronic means where appropriate, or by other means
- Upon request from the data subject, the information can be provided orally
Furthermore, Article 12(5) of the GDPR states that the provision of information must be free of charge. Check whether your company’s privacy policy meets the above criteria and revise it as necessary.
Key Points for Revising Privacy Policies in Compliance with GDPR

The GDPR specifies multiple items that data controllers must explicitly disclose to data subjects when collecting personal data directly from the data subjects (Article 13 of the GDPR) and when obtaining personal data from sources other than the data subjects (Article 14 of the GDPR).
The items that data controllers must explicitly disclose include the following:
- The identity and detailed contact information of the controller
- If there is a representative, the identity and detailed contact information of the representative
- The rights of the data subject to access, rectify, erase, restrict processing, data portability, and to object
- The purposes of processing personal data and the legal basis for processing
- The period for which personal data will be stored, or the criteria used to determine that period
- The categories of personal data concerned
Some of the items to be disclosed are not present in Japanese privacy policies, so it is essential to focus on revising these aspects. For information on privacy policies based on the Japanese Personal Information Protection Law, please refer to the following article.
Related article: What are the Key Points When Creating a Privacy Policy Based on the Personal Information Protection Law?[ja]
Here, we will explain the key points for revision, focusing on aspects not covered by privacy policies based on the Japanese Personal Information Protection Law.
Legal Basis for Data Processing
Under the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), there is a mandatory requirement to explicitly state the “legal basis for data processing,” which was not specified under the Japanese Personal Information Protection Law. The legal grounds for the lawful handling of personal data are as follows (Article 6 of the GDPR):
- Consent of the data subject
- Performance of a contract
- Legal obligation
- Vital interests
- Public interest
- Legitimate interest
If one of the above six grounds applies, the data processing is considered lawful, so it is important to clearly state this in your privacy policy. For individuals from whom you are collecting information for the first time, you can comply by obtaining their consent through a new privacy policy.
However, attention must be paid to users who have already given their consent. For those who had agreed before the revision of the privacy policy, it may be necessary to obtain their consent again.
In such cases, one approach is to list one of the six legal grounds in the privacy policy and obtain consent for the revision accordingly.
Categories of Collected Information and Purposes of Use
Traditional privacy policies often listed the types of information collected, the purposes of use, and the terms of use all on the same page, generally obtaining consent in a bundled form. However, under the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), it is required to clarify what the users are consenting to, making the subjects of consent explicit.
It is advisable to specify the purpose of use for each category of collected information and to employ a display format that seeks consent for each separately.
Clarification of Purpose of Use
Under the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), it is required to clearly indicate the purpose for which collected information is used. For instance, a purpose described as “to improve services” may be deemed too vague and thus inappropriate.
Furthermore, any additional handling of data that does not align with the stated purpose is not permitted. Therefore, it is important to pay careful attention when revising your privacy policy to ensure compliance.
Right to Erasure and Data Portability
Many companies have traditionally included rights of access and rectification in their privacy policies. However, under the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), it is also required to mention the ‘Right to Erasure and Data Portability’.
The Right to Erasure refers to the right of individuals to have their personal data deleted by the administrator. The Right to Data Portability refers to the right to transfer personal data to another service.
For example, this includes transferring subscriber data and historical data from mobile phone company A to mobile phone company B. To comply with the GDPR, it is necessary to include these rights in your privacy policy.
Clarification of Data Retention Periods
Under the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), it is now required to specify the ‘retention period for personal data,’ which was not traditionally included in privacy policies. If it is not possible to determine the retention period, the regulation allows for the clarification of the criteria used to determine how long the data will be stored.
Status of GDPR Compliance Among Japanese Companies

We would like to introduce survey information from the “Corporate IT Utilization Trends Survey 2021 Detailed Results” conducted by the Japan Information Economy Society Promotion Association and ITR Corporation. You can find the survey here: 「企業IT利活⽤動向調査2021」集計結果(詳細版)[ja].
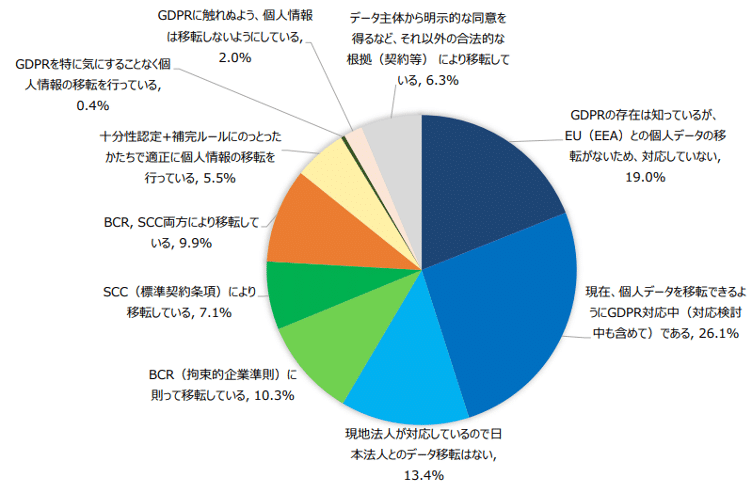
According to the survey results, few companies are currently compliant with the GDPR, and the majority, at 26.1%, are in the process of considering compliance. As of the 2021 survey, there is also a trend of many companies not transferring personal data to the EU.
The survey results regarding the exchange of personal data with the EU are as follows:
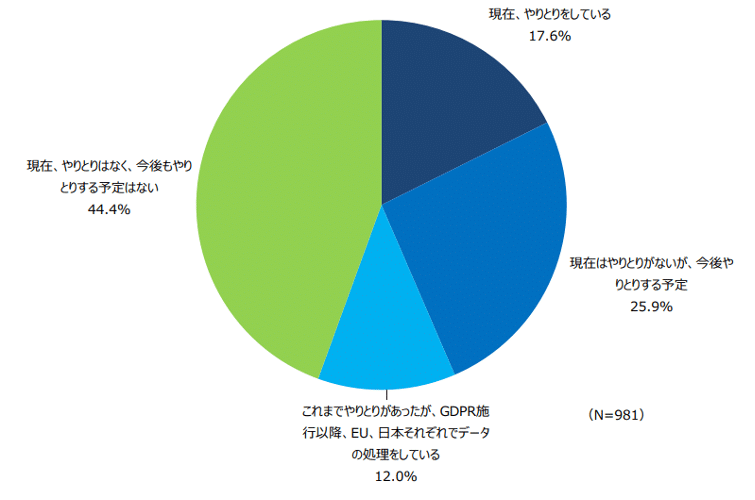
As seen in the figure above, the largest group of companies, at 44.4%, responded that they “currently have no exchanges and have no plans to do so in the future.” 12% of companies indicated that they “had exchanges in the past, but since the implementation of the GDPR, they are processing data separately in the EU and Japan.”
Those who stated “currently no exchanges but planning to in the future” accounted for 25.9%, and “currently exchanging” was at 17.6%. This suggests that while there is potential for an increase in companies engaging with the EU in the future, the number was still low at the time of the 2021 survey.
Source: JIPDEC/ITR “Corporate IT Utilization Trends Survey 2021″[ja]
How Top Companies Comply with GDPR

Many are unsure about what to include when revising their privacy policies to comply with the GDPR. In this section, we will provide a detailed explanation of how top companies, specifically Google and Facebook, have addressed GDPR compliance.
Google’s GDPR Compliance Efforts
Google has announced the following measures to comply with the GDPR:
- Enhanced transparency for users
- Improved user control over their data
- Increased data portability
- Improved tools for parental consent and safe internet usage for children
- Support for business users and partners
- Strengthened privacy compliance programs
Here, we will explain the details.
Reference: Google “Our preparations for Europe’s new data protection law (GDPR)[ja]“
Enhancing Transparency for Users
Google is improving and updating its privacy policy to make it easier for users to understand the information it collects and the reasons behind it, as well as to make this information more accessible. Other updates include the following:
- Adding details on how to manage, export, and delete information
- Incorporating videos and diagrams in addition to text
Furthermore, changes have been made to allow easier access to the privacy settings page.
Improving User Management
In response to the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), we have improved our user management methods. The changes are as follows:
- Ability to view and delete data in My Activity
- Added functionality to search by topic, date, and product
- Ability to review privacy settings that suit individual preferences
- Control and hide the ads displayed
- Understanding of data through the Google Dashboard
Furthermore, even before the enforcement of the GDPR, changes have been made to simplify the management of user information and advertisements.
Enhancing Data Portability
Google offers a variety of services such as Google Photos, Drive, Calendar, and Gmail. The following are measures Google has implemented to enhance data portability in compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Expansion of services and management options that support data downloading
- Introduction of features that allow scheduling of regular downloads
Enhancing Tools for Parental Consent and Appropriate Internet Use by Children
At Google, the Family Link app is provided to support parents in managing their children’s appropriate use of the internet. Through Family Link, parents can create accounts for their children.
The app features options such as “managing usage time” and “temporarily pausing devices,” enabling parents to set and manage rules within the home.
Support for Business Users & Partners
To comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), we have updated our policies concerning how Google partners (such as advertisers and website operators) request user consent within their sites and apps. Other notable updates include:
- Provision of tools to support GDPR compliance
- Stricter certification processes for companies using Google’s advertising services
- Updated data processing terms
- Providing detailed information on data portability and data incident notifications
Enhancing the Privacy Compliance Program
In response to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), we are enhancing our privacy compliance program. The enhancements include the following:
- Improving the privacy program
- Strengthening the product review process
Furthermore, we are also documenting our data processing activities more comprehensively.
Facebook’s GDPR Compliance
Facebook has announced the following measures in response to the GDPR:
- Verification of information acquisition from displayed ads
- Choice of profile information
- Verification of facial recognition technology (EU & Canada)
- Updated terms of service & data agreements
- Introduction of features that make accessing, deleting, and downloading information easy
- Information provision for younger users
Here, we will explain the details.
Reference: Facebook “Compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Provision of New Privacy Protections[ja]“
Verification of Information Acquisition from Displayed Ads
Facebook’s partners use information obtained from clicks on the ‘Like’ button and tools provided by Facebook for ad displays. Users are provided with information about the ads and can choose whether to allow partners to use this information for ad displays.
Choice of Profile Information
Facebook profiles may contain and display information about political views, religion/beliefs, and relationships. Users can choose whether to “continue to make this information public” and whether “the information being public can be used for ads.”
Profile information can always be freely chosen, and if the user wishes, it can be easily deleted.
Verification of Facial Recognition Technology (EU & Canada)
Facebook allows users in EU member states and Canada to choose whether to use facial recognition technology. Users in other regions also have the freedom to choose.
Updated Terms of Service & Data Agreements
Users will see prompts to agree to the “Terms of Service” and “Data Policy” that include detailed information about the mechanics of the service.
Introduction of Features that Make Accessing, Deleting, and Downloading Information Easy
With the use of the “Personal Data Management Tool,” users can review and delete their data. They can also easily download and export their data.
The log function for mobile device activities has been updated to make it easier for users to check what information they have shared in the past.
Information Provision for Younger Users
Facebook already has restrictions in place for teenage users, which include:
- Limited ad categories
- No use of facial recognition (under 18)
- Limited visibility and searchability of information shared by teenage users
Additionally, the default settings are designed so that information is not “public.”
In response to the GDPR, Facebook has set additional regulations. For users in EU member states, parental consent is required for ad viewing and profile entries (such as religion/beliefs, political views). In other regions, users can choose whether they want to use data obtained from partners for ad displays and whether to make personal information public on their profiles.
Summary: GDPR Requires a Broader Scope of Personal Data Protection Compared to Japanese Law

The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) includes various provisions such as ‘clarification of the purpose for each piece of information collected,’ ‘explicit rights to erasure and data portability,’ and ‘clearly defined retention periods,’ which extend the scope of user rights beyond what traditional Japanese law offers.
In the event of a GDPR violation, companies may face substantial fines and must comply with GDPR when handling personal information within the EU. Companies that are operating or considering expansion within the EU should create privacy policies in line with GDPR requirements.
Guidance on Measures by Our Firm
Monolith Law Office is a legal practice with extensive experience in IT, particularly in both the internet and legal fields. In recent years, global business has been expanding increasingly, and the need for expert legal checks is growing more than ever. Our firm provides solutions related to international legal affairs.
Areas of practice at Monolith Law Office: International Legal Affairs & Overseas Business[ja]





















